Language Modeling
Technical Program Session SPE-4
CAPITALIZATION NORMALIZATION FOR LANGUAGE MODELING WITH AN ACCURATE AND EFFICIENT HIERARCHICAL RNN MODEL
Google Research
Problem
Capitalization normalization (truecasing) is the task of restoring the correct case (uppercase or lowercase) of noisy text.
Proposed method
A fast, accurate and compact two-level hierarchical word-and-character-based RNN
Used the truecaser to normalize user-generated text in a Federated Learning framework for language modeling.

Key Findings
In a real user A/B experiment, authors demonstrated that the improvement translates to reduced prediction error rates in a virtual keyboard application.
NEURAL-FST CLASS LANGUAGE MODEL FOR END-TO-END SPEECH RECOGNITION
Facebook AI, USA
Proposed method
Neural-FST Class Language Model (NFCLM) for endto-end speech recognition
a novel method that combines neural network language models (NNLMs) and finite state transducers (FSTs) in a mathematically consistent framework
Key Findings
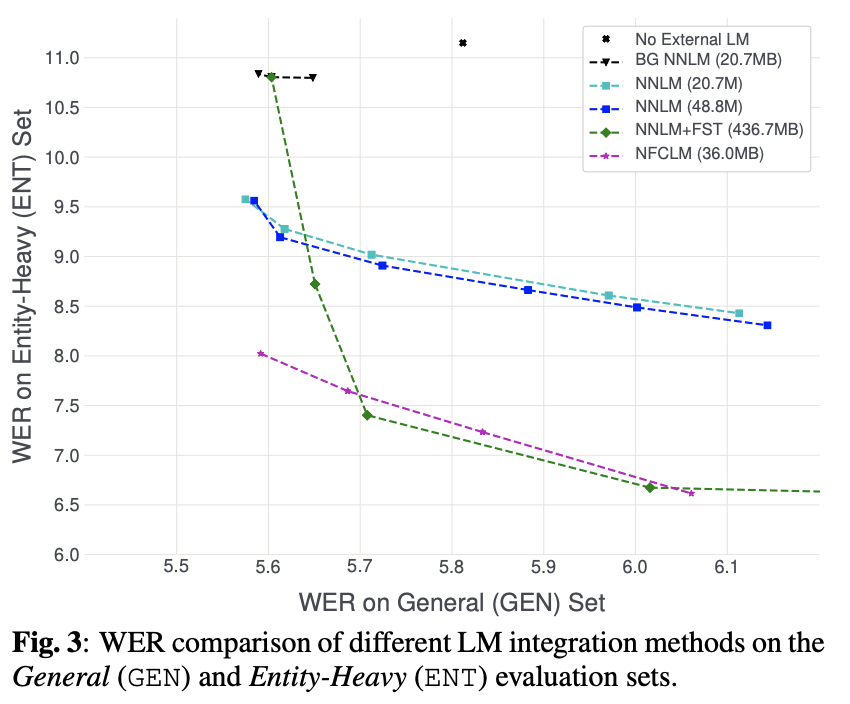
NFCLM significantly outperforms NNLM by 15.8% relative in terms of WER.
NFCLM achieves similar performance as traditional NNLM and FST shallow fusion while being less prone to overbiasing and 12 times more compact, making it more suitable for on-device usage.
ENHANCE RNNLMS WITH HIERARCHICAL MULTI-TASK LEARNING FOR ASR
University of Missouri, USA
Proposed method
Key Findings
RESCOREBERT: DISCRIMINATIVE SPEECH RECOGNITION RESCORING WITH BERT
1Amazon Alexa AI, USA 2Emory University, USA
Problem
Second-pass rescoring improves the outputs from a first-pass decoder by implementing a lattice rescoring or n-best re-ranking.
Proposed method (RescoreBERT)
Authors showed how to train a BERT-based rescoring model with minimum WER (MWER) loss, to incorporate the improvements of a discriminative loss into fine-tuning of deep bidirectional pretrained models for ASR.
Authors proposed a fusion strategy that incorporates the MLM into the discriminative training process to effectively distill knowledge from a pretrained model. We further propose an alternative discriminative loss.

Key Findings
Reduced WER by 6.6%/3.4% relative on the LibriSpeech clean/other test sets over a BERT baseline without discriminative objective
Found that it reduces both latency and WER (by 3 to 8% relative) over an LSTM rescoring model.
Hybrid sub-word segmentation for handling long tail in morphologically rich low resource languages
Cognitive Systems Lab, University Bremen, Germany
Problem
Dealing with Out Of Vocabulary (OOV) words or unseen words
For morphologically rich languages having high type token ratio, the OOV percentage is also quite high.
Sub-word segmentation has been found to be one of the major approaches in dealing with OOVs.
Proposed method
This paper presents a hybrid sub-word segmentation algorithm to deal with OOVs.
A sub-word segmentation evaluation methodology is also presented.
All the experiments are done for conversational code-switched Malayalam-English corpus.